Higher-Order Multicuts for Geometric Model Fitting and Motion Segmentation
Evgeny Levinkov*, Amirhossein Kardoost*, Bjoern Andres, Margret Keuper
TPAMI · 2022 · (* Contributed equally)
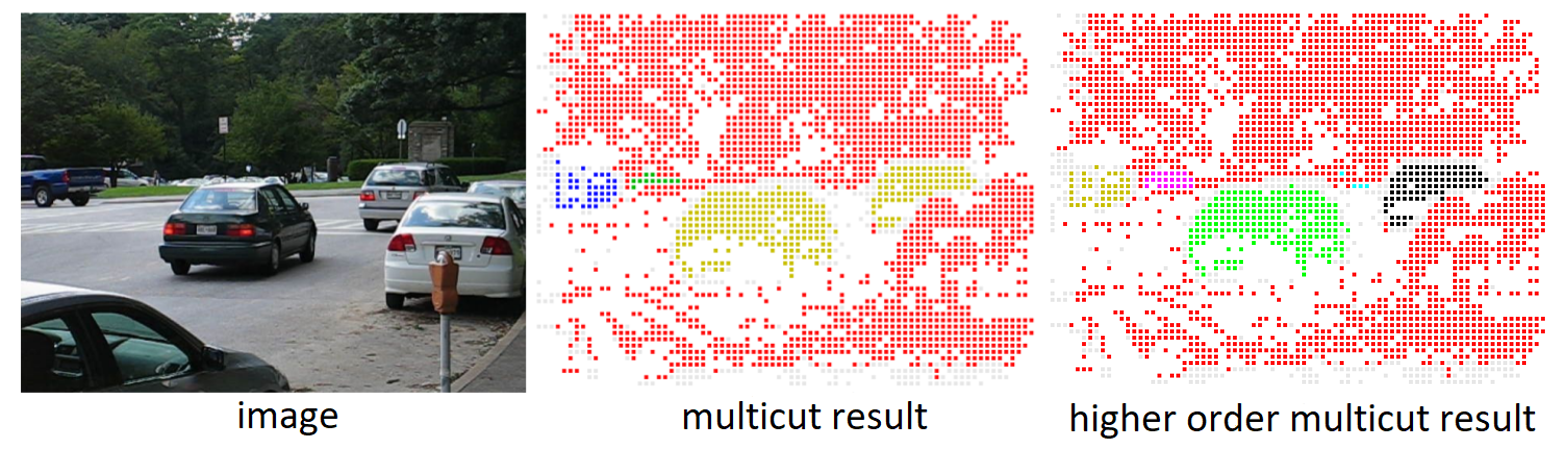
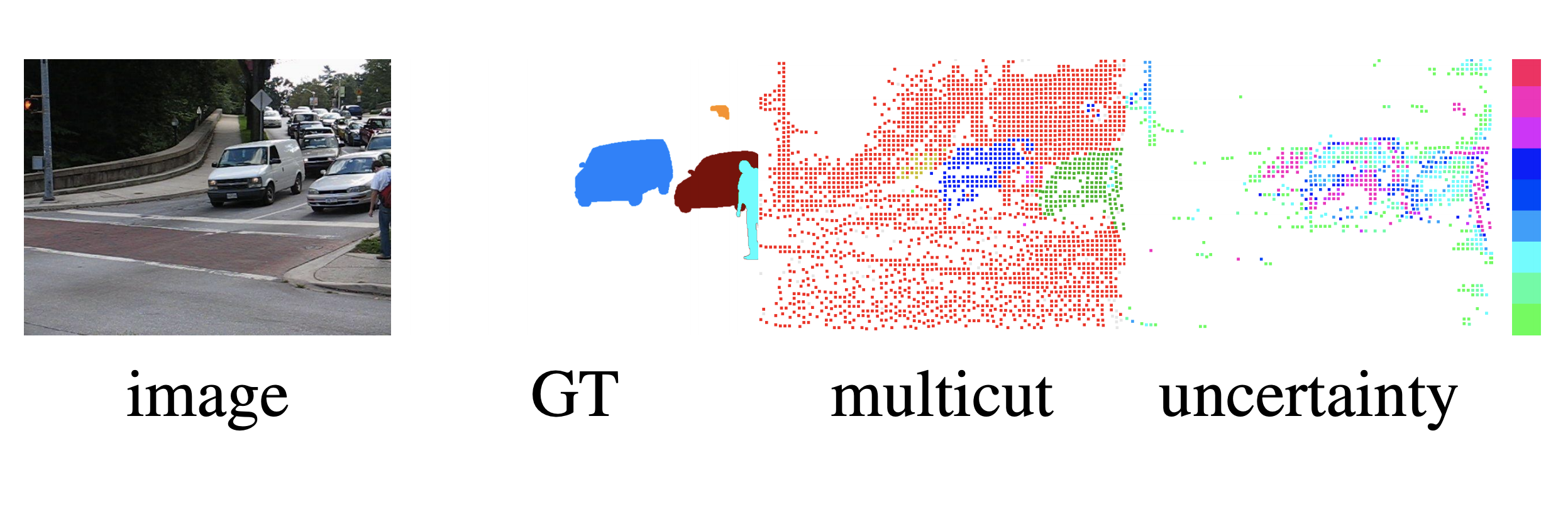
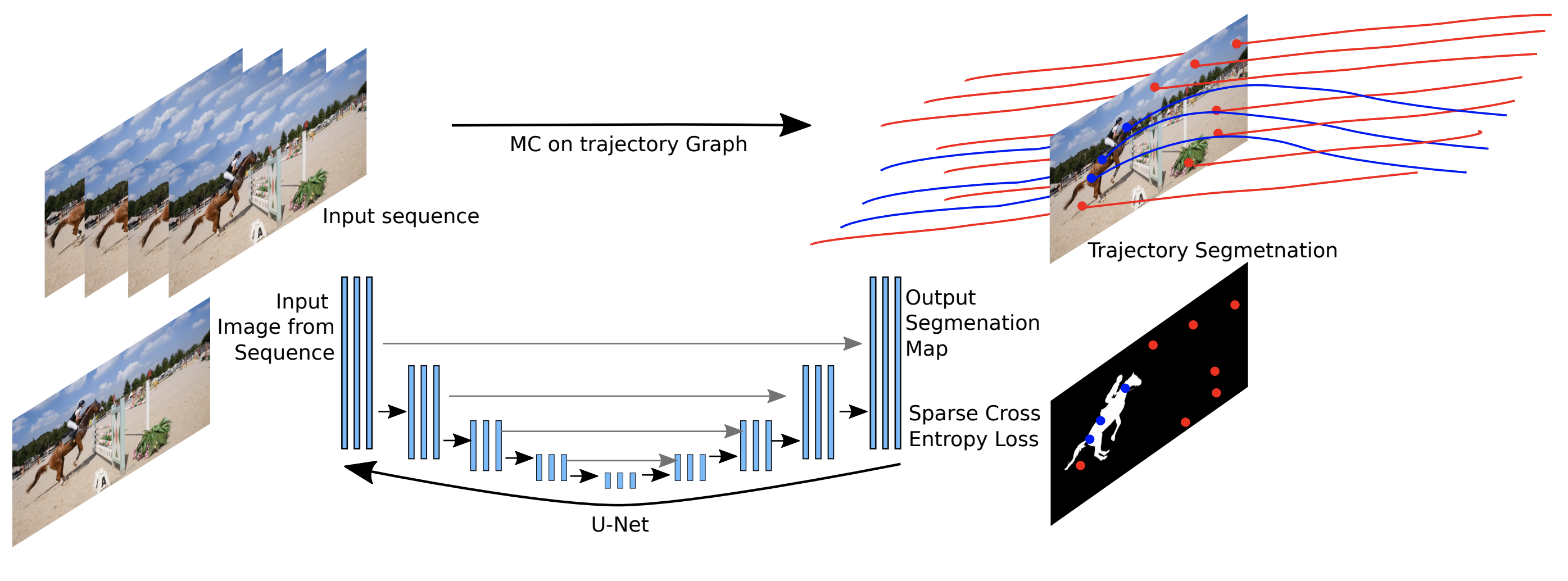
The minimum cost lifted multicut problem is a generalization of the multicut problem (also known as correlation clustering) and is a means to optimizing a decomposition of a graph w.r.t. both positive and negative edge costs. It has been shown to be useful in a large variety of applications in computer vision thanks to the fact that multicut-based formulations do not require the number of components given a priori; instead, it is deduced from the solution. However, the standard multicut cost function is limited to pairwise relationships between nodes, while several important applications either require or can benefit from a higher-order cost function, i.e. hyper-edges. In this paper, we propose a pseudo-boolean formulation for a multiple model fitting problem. It is based on a formulation of any-order minimum cost lifted multicuts, which allows to partition an undirected graph with pairwise connectivity such as to minimize costs defined over any set of hyper-edges. As the proposed formulation is NP-hard and the branch-and-bound algorithm (as well as obtaining lower bounds) is too slow in practice, we propose an efficient local search algorithm for inference into resulting problems. We demonstrate versatility and effectiveness of our approach in several applications: 1) We define a geometric multiple model fitting, more specifically, a line fitting problem on all triplets of points and group points, that belong to the same line, together. 2) We formulate homography and motion estimation as a geometric model fitting problem where the task is to find groups of points that can be explained by the same geometrical transformation. 3) In motion segmentation our model allows to go from modeling translational motion to Euclidean or affine transformations, which improves the segmentation quality in terms of F-measure.
@article{kardoost_tpami_2022,
author = {Levinkov, Evgeny and Kardoost, Amirhossein and Andres, Bjoern and Keuper, Margret},
journal = {Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)},
title = {Higher-Order Multicuts for Geometric Model Fitting and Motion Segmentation},
year = {2022},
doi = {10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3148795}
}